How does prostate cancer treatment affect mental health?

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy
Cancer Archive
Articles
Newer drugs are improving survival for men with metastatic prostate cancer
Men with prostate cancer that has spread outside the gland now have several newer drug options available for treatment, and research has found that taking any of them is likely to improve survival duration.
A more precise approach to fighting cancer
Precision medicine offers a personalized approach for prevention and treatment of cancer and other diseases.
Image: © Pogotskiy/Thinkstock
If you have a stomachache or cold, you go to the pharmacy and grab the same remedy that everyone else uses, and it often works. But is that always the best approach? Your reaction to an infection may be quite different from someone else's, so perhaps you need a treatment designed just for you and your ailment.
That's the philosophy behind precision medicine (sometimes referred to as personalized medicine), an emerging approach to prevention and treatment that takes into account a person's genes, environment, and lifestyle and eliminates the one-size-fits-all approach to health care.
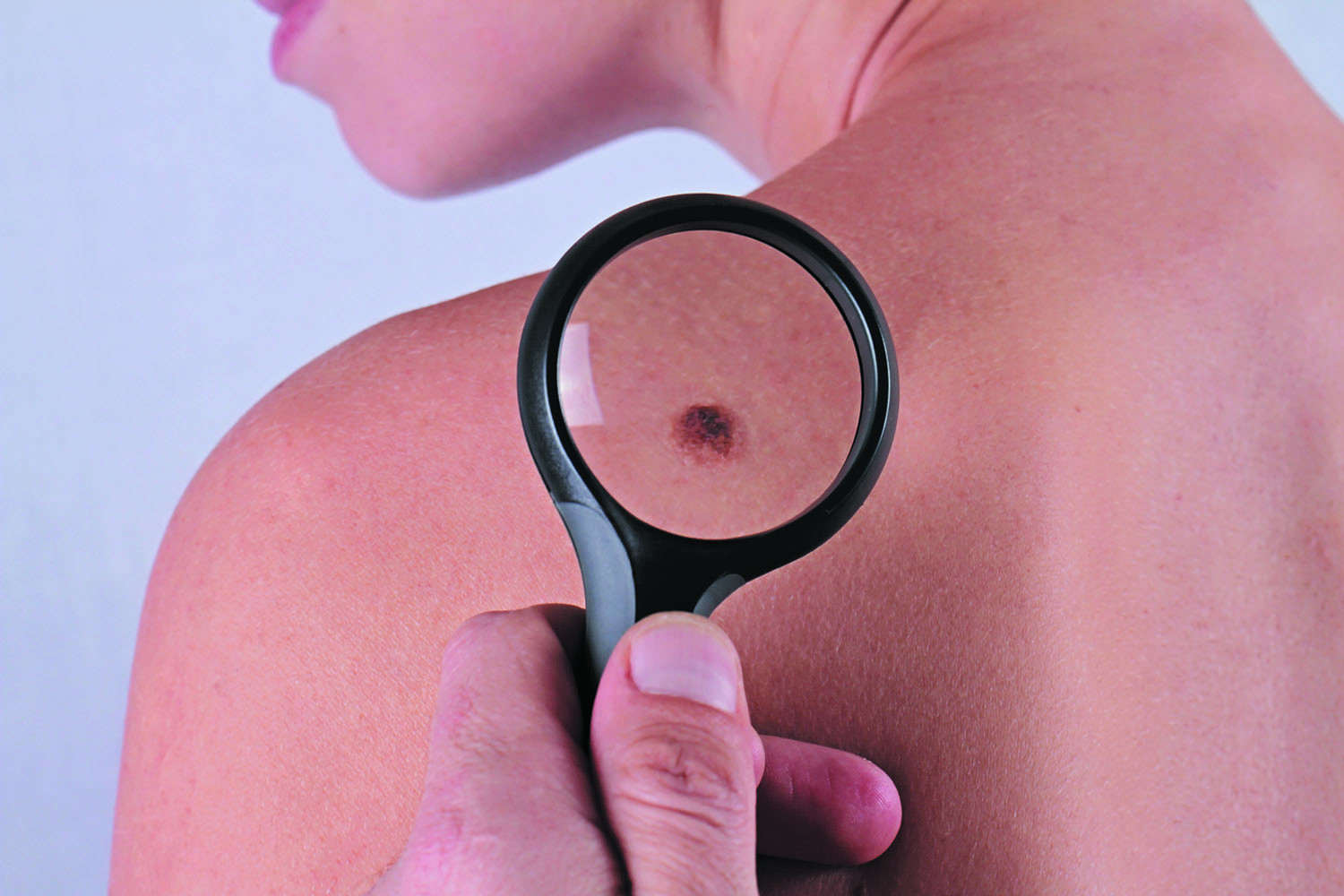
Melanomas don’t always arise from existing moles
In the journals
Image: © Manuel-F-O/Thinkstock
While it's important to have any suspicious mole checked for possible skin cancer, a study published online Aug. 29, 2017, by the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology suggests most melanomas — the deadliest skin cancer — appear as new spots on the skin. The researchers reviewed 38 studies involving 20,126 cases of melanoma and found that 29% of diagnosed melanomas came from an existing mole, while 71% appeared as new spots. Moreover, they discovered that melanomas that grew from moles were thinner and thus less aggressive than other melanomas. In fact, people whose melanoma was associated with a mole had a better prognosis than others.
The study's authors stressed the importance of looking for any new spots on the skin as well as checking moles for changes, like itching or bleeding, and to see a dermatologist if needed. The American Academy of Dermatology encourages everyone to perform regular skin self-exams, and to ask a partner to check hard-to-see areas like the back. You can learn how to do a skin self-exam, and much more, at www.aad.org/public/spot-skin-cancer.
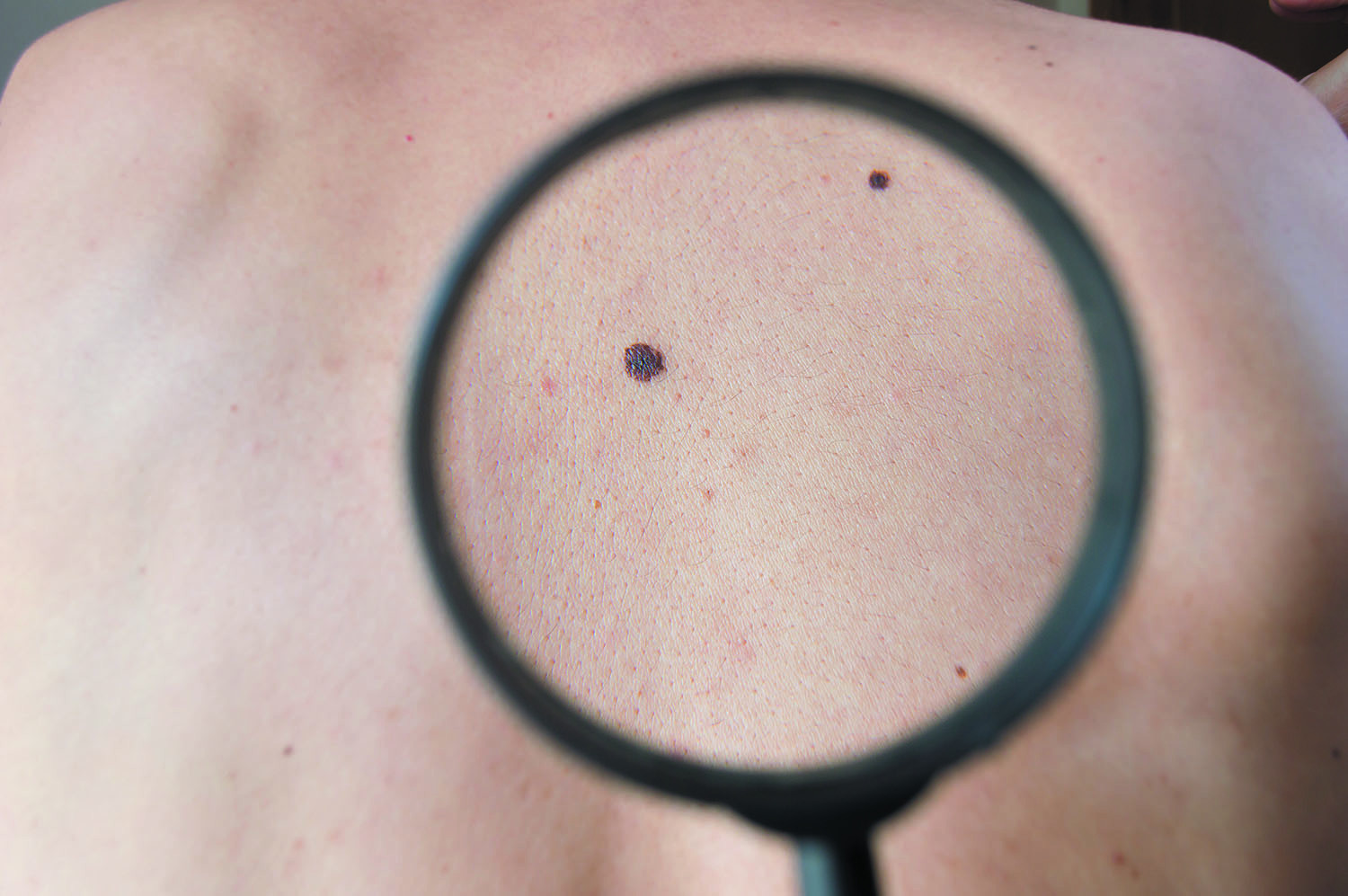
Most melanomas start as new spots
Research we're watching
Image: © ChesiireCat/Thinkstock
To catch skin cancer early, be on the lookout for new spots on your skin. A recent study found that more often than not, melanoma occurs as a new spot on your body — not as changes in an existing mole. The study, published online August 29 by the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology, found that only 29% of melanomas came from an existing mole on the body that changed. In 71% of cases, melanoma occurred in a new lesion that popped up in a new place on the skin. In addition, the study authors noted that melanomas that do occur in existing moles tend to be thinner than melanomas in new lesions.
In addition to looking for new and unusual spots on your skin, remember your ABCDs to spot the signs of melanoma:
Cancer report shows progress, fewer cancer deaths
Research we're watching
Good news on the cancer front: The cancer death rate dropped 35% between 1991 and 2014 among children and 25% in adults, according to the annual American Association for Cancer Research Cancer Progress Report. And more treatments for the disease are on the horizon. The FDA has recently approved nine new cancer treatments and signed off on expanding the uses of eight existing therapies to treat different types of cancer. Among the new treatments are innovative immunotherapeutics, which help some people with cancer live longer with a better quality of life; an imaging agent that will let surgeons more precisely remove brain tumors; and molecularly targeted agents, which take aim at specific molecules that help cancers grow and spread to other areas of the body. It is hoped that these new treatments will further reduce cancer deaths. To read the full report, go to cancerprogressreport.org.
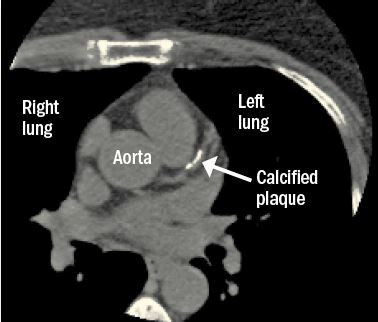
When you look for cancer, you might find heart disease
Screening tests for lung and breast cancer—chest computed tomography (CT) scans and mammograms—may offer clues about a person’s risk of heart disease.
B vitamins may raise risk of lung cancer in men who smoke
In the journals
Smoking causes lung cancer — no surprise there. But a new study found that high dosages of vitamin B6 or B12 supplements were associated with three to four times the lung cancer risk in male smokers compared with smokers who did not take the supplements. The results were published in the Aug. 22, 2017, Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers examined information from more than 44,000 men ages 50 to 76. At enrollment, the men reported on their smoking history and their B vitamin supplement use over the previous 10 years. In the study, high intake of B vitamin was classified as 20 milligrams (mg) of B6 per day or 55 micrograms (mcg) of B12. (The recommended daily intakes for men ages 51 and older are 1.7 mg for B6 and 2.4 mcg for B12.)

How does prostate cancer treatment affect mental health?

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up