How does prostate cancer treatment affect mental health?

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy
Sleep Archive
Articles
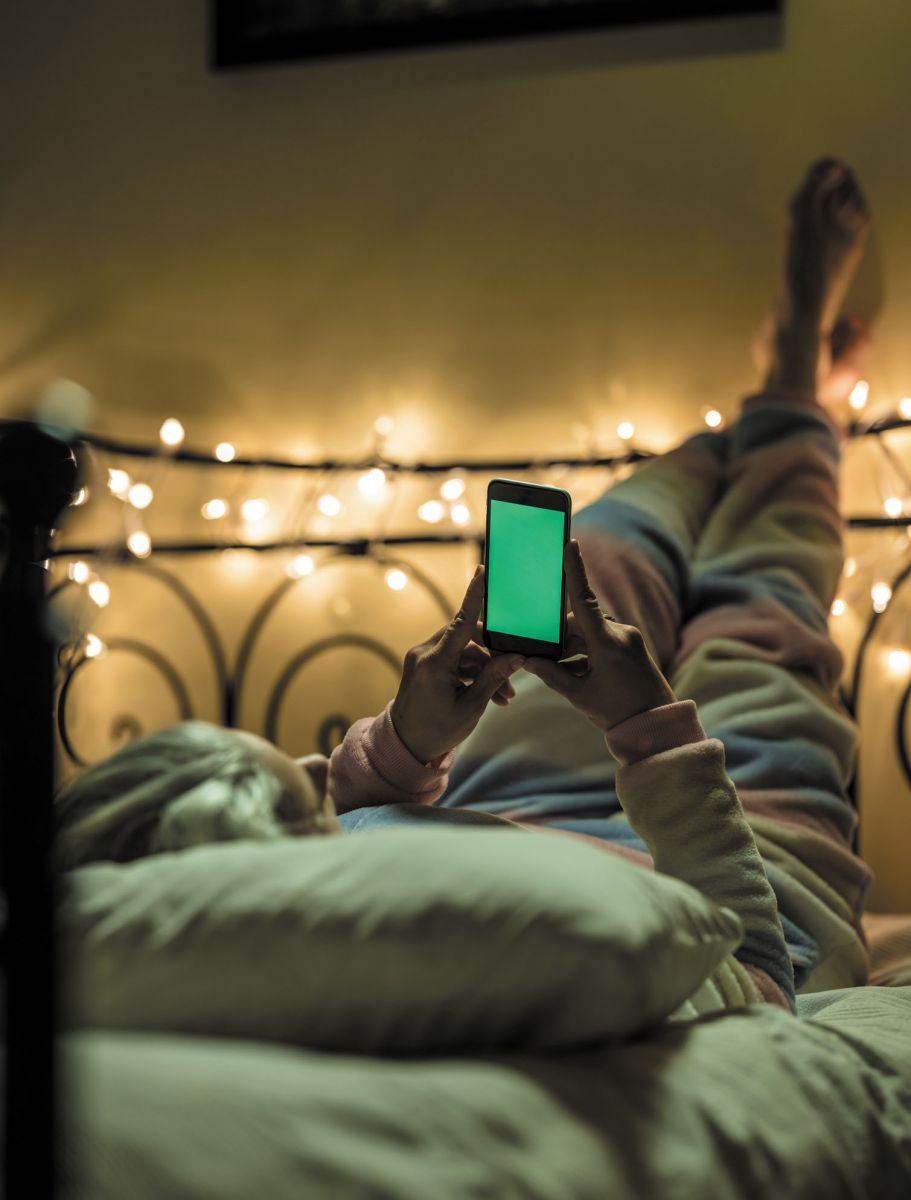
Bedtime screen time may reduce sleep quality
Research we're watching
Is your smartphone reducing your sleep quality? The National Sleep Foundation's most recent Sleep Health Index found that people who used technology such as phones, tablets, or computers in bed before they went to sleep scored lower on measures of sleep quality than those who didn't. Nearly 50% of American adults polled said they used technology in bed at least once a week, and nearly 30% said they did so every day. Some 21% of adults even said if they woke up during the night they would check their devices before going back to sleep. The National Sleep Foundation says to ensure the best sleep quality, it's best to leave digital distractions for the daytime hours and keep them out of bed.
Image: © Sisoje/Getty Images
Trouble keeping information in mind? Could be sleep, mood — or age
Most people experience some degree of decreased memory as they get older, but memory performance is also affected by mood and sleep quality, and these are factors that can be controlled and improved.
By the way, doctor: Is it okay to take ibuprofen p.m.?
Q. I take ibuprofen p.m. on occasion — maybe once a month or so — to help me get to sleep. It seems to work. Is that okay?
A. Ibuprofen p.m. is a combination medication that contains ibuprofen and diphenhydramine, which is the active ingredient in Benadryl, an antihistamine taken for allergies.
Trouble keeping information in mind? Could be sleep, mood, or age
Most people experience some degree of decreased memory as they get older, but memory performance is also affected by mood and sleep quality, and these are factors that can be controlled and improved.
Sleeping in on the weekend won't help you recover from lost sleep
Research we're watching
Many people skimp on sleep during the week and try to make up for lost time on the weekend. But a study published February 28 in Current Biology shows this strategy won't necessarily reverse the ill effects of sleep deprivation on your body.
The study, conducted in a sleep lab, tested the health effects of three sleep strategies over a two-week period. Participants in one group were allowed to sleep up to nine hours a night. Those in a second group were limited to five hours a night. People in the third group slept five hours nightly during the week, but were allowed to sleep in on Saturday and Sunday.
Four keys to prevent cardiovascular disease
Are you doing everything you can to keep your heart healthy?
After decades of steady decline, the number of deaths from cardiovascular disease (CVD) has risen over the past few years, according to the American Heart Association.
The good news is that an estimated 80% of all CVD cases — heart disease, heart attack, heart failure, and stroke — can be prevented. The key is to control high blood pressure and high cholesterol and to maintain healthy habits, such as exercising regularly, eating a plant-based diet, getting enough sleep, and not smoking.
Poor sleep can change your reaction to pain
In the journals
Lack of sleep may make you more sensitive to pain, according to a study in the Jan. 28, 2019, issue of The Journal of Neuroscience.
Researchers found that poor sleep interferes with certain pain centers of the brain and can change how a person perceives and reacts to discomfort. In the study, scientists scanned the brains of 25 healthy adults in two sleep environments: first, after they slept eight hours, and again after they were kept awake for 24 to 28 hours. During both scans, they also received uncomfortable levels of heat to their legs.
How a good night's sleep might help your heart
Research we're watching
Sleep has long been known to help protect you against heart disease, and researchers now think they know at least one reason why. A study published online February 13 by the journal Nature looked at how sleep duration and quality relates to the buildup of damaging plaque in the arteries.
Harvard Medical School researchers found that a lack of good sleep boosts the body's production of inflammatory white blood cells that earlier research has linked to fatty buildup in the arteries. This could help explain why sleep problems can lead to arterial buildup. Poor sleep is linked not only to clogged arteries, but also to a host of chronic health conditions, such as cancer, obesity, and diabetes — all good reasons to make sure you get your z's.
Answers to the top questions about cannabis extract
Sales of cannabidiol-infused products are expected to top $2 billion by 2021. But is CBD right for you?
Cannabidiol (CBD) is touted as a natural wonder that can help treat symptoms of everything from anxiety to arthritis pain. The plant extract comes from two varieties of cannabis — hemp and marijuana — and is available in creams, tinctures, oils, patches, gummy bears, capsules, and more. You can even add CBD to a latte if you walk into a coffee shop in some cities.
But is CBD safe for older adults? There haven't been a lot of large studies of CBD's safety, but more traditional medicines for pain and anxiety are not free of adverse effects, either. "I think CBD is likely safer than many other treatments people use for pain, insomnia, or anxiety," says Dr. Peter Grinspoon, a primary care physician with Harvard-affiliated Massachusetts General Hospital. Other physicians don't think we know enough about the safety profile of CBD to be sure.
Sleep shortfall linked to higher risk of clogged arteries
Research we're watching
Too little sleep may be hard on your blood vessels, according to a study in the January issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
For the study, 3,974 healthy, middle-aged people wore watchlike devices called actigraphs for a week to track how long they slept and how often they woke up and moved during the night. The participants also received three-dimensional ultrasounds of arteries in their necks and upper legs and special scans to check their heart arteries.

How does prostate cancer treatment affect mental health?

5 timeless habits for better health

What are the symptoms of prostate cancer?

Is your breakfast cereal healthy?

When pain signals an emergency: Symptoms you should never ignore

Does exercise give you energy?

Acupuncture for pain relief: How it works and what to expect

How to avoid jet lag: Tips for staying alert when you travel

Biofeedback therapy: How it works and how it can help relieve pain

Best vitamins and minerals for energy
Free Healthbeat Signup
Get the latest in health news delivered to your inbox!
Sign Up